Versions Compared
| Version | Old Version 35 | New Version 36 |
|---|---|---|
| Changes made by | ||
| Saved on |
Key
- This line was added.
- This line was removed.
- Formatting was changed.
As a Farmer I want to purchase items from a shop and make payments using the Helium app
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Lesson Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you should:
- Be comfortable using visibility bindings to hide and show view components based on unit variables and functions
- Know what is required in order to make payments from an app and to track the status of these payments
- Know how to use the pay and payWithRef built-in functions
- Know how to use payment callback functions
App Use Case Scenario
The app use case for this lesson is that a farmer would like to make purchases from a specific shop using the application. This includes making a payment to the shop using the Helium payments framework.
Firstly, a farmer will select a shop and use a submit button to confirm his selection. The view will then be updated to display a table of all the stock items that a shop has in stock. This includes the name of the item, the current stock level and the current unit price for the stock item. The farmer will then select a stock item using a row action on this table.
Once this selection has been made, the view will again be updated to include info widgets showing the currently selected stock item, its stock level and unit price as well as a text area where the farmer can specify the quantity of the item he would like to purchase. Another submit button to calculate the total cost of the selection can then be pressed.
Once this has been done additional view components appear. These components describes a summary of the price for the goods, the discount offered if the farmer has previously uploaded a government assistance certificate and the final cost to the farmer. Once the farmer confirms this, the payment will be recorded and sent to Helium for processing using the payment framework.
Modified or Added App Files
Modified or AddedThe files in the tutorial app that were modified or added as part of this lesson are as follows:
./model/objects/Shop.mez
./model/objects/FarmerPurchase.mez
./web-app/presenters/farmer_ops/FarmerPurchases.mez
./web-app/views/farmer_ops/HistoricFarmerPurchases.vxml
./web-app/views/farmer_ops/NewFarmerPurchase.vxml
./web-app/views/user_management/ShopOwnerDetails.vxml
./web-app/views/user_management/ShopOwnerUserMgmt.vxml
./web-app/lang/en.lang
./services/PaymentCallbacks.mez
Data Model Additions for Farmer Purchases
Only two additions to our date model is required. Firstly, an object to keep track of purchases made by farmers. This object needs to keep track of the purchase details such as item that was purchased, unit cost, discount and final cost. It also needs to keep track of the internal Helium payment status and id. This is discussed further later in this lesson. Further more, the object also need to keep track of the farmer, shop and stock item that was involved in the transaction.
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
persistent object FarmerPurchase {
// When was the purchase made
datetime purchasedOn;
// Quantity and cost of purchase
int quantity;
decimal unitPrice;
decimal goodsCost;
decimal discount;
int finalCost;
// Helium provided payment status and id
datetime paymentStatusUpdatedOn;
PAYMENT_STATUS paymentStatus;
uuid paymentId;
// Stock item that was purchased
@ManyToOne
Stock stock via purchases;
// Farmer that made the purchase
@ManyToOne
Farmer farmer via purchases;
// Shop at which purchase was made
@ManyToOne
Shop shop via purchases;
} |
Lastly, we also need to add a mobile number attribute to the Shop object. This is required for making payments to a specific shop.
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
@requiredFieldValidator("validator.required_field")
string mobileNumber; |
Overview of View and Unit Additions for Making Purchases
For the implementation of this feature we have added the NewFarmerPurchase view. This view has a menu item for the farmer role and is thus accessible from the main app menu. This single view will be used by the farmer to perform purchases from specific shops.
In addition a view containing all historic records, namely HistoricFarmerPurchaes, is also added and is accessible from an action button on the NewFarmerPurchase view.
These two views are backed by the FarmerPurchases presenter file and unit.
Widget Visibility
As mentioned in the scenario that accompanies this lesson, we will have multiple stages within the flow of the purchase feature. Despite this we will only be using one view. After each stage, more view components become visible to the user. This is achieved using "visbile" function bindings. The following code snippet shows the functions that are used for these bindings:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
// Once a shop has been selected, the stock items for this shop can be displayed
bool showStockTable() {
if(shop == null) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Once a stock item has been selected is can be displayed with a text field for the quantity to purchase
bool showPurchaseForm() {
if(showStockTable() == false || selectedStock == null) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Once the purchase quantity has been validated and the price calculated the cost summary can be displayed
bool showSummary() {
if(showPurchaseForm() == false || goodsCost == null) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
// In the case of a farmer with a government assistance certificate the discount related to this should
// also be shown as part of the final cost summary
bool governmentAssitanceApplicableAndSummary() {
if(showSummary() == false || farmer.governmentAssistanceCertificate == null) {
return false;
}
return true;
} |
The screenshots below show the difference stages of widget visibility for the NewFarmerPurchase view:
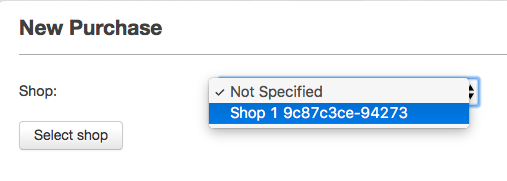 Image Added
Image Added
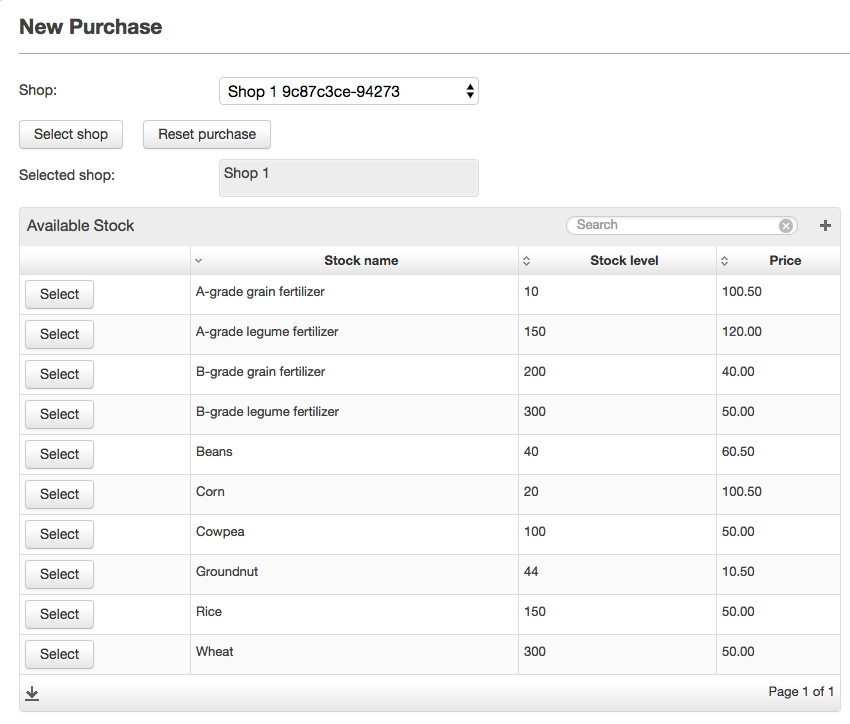 Image Added
Image Added
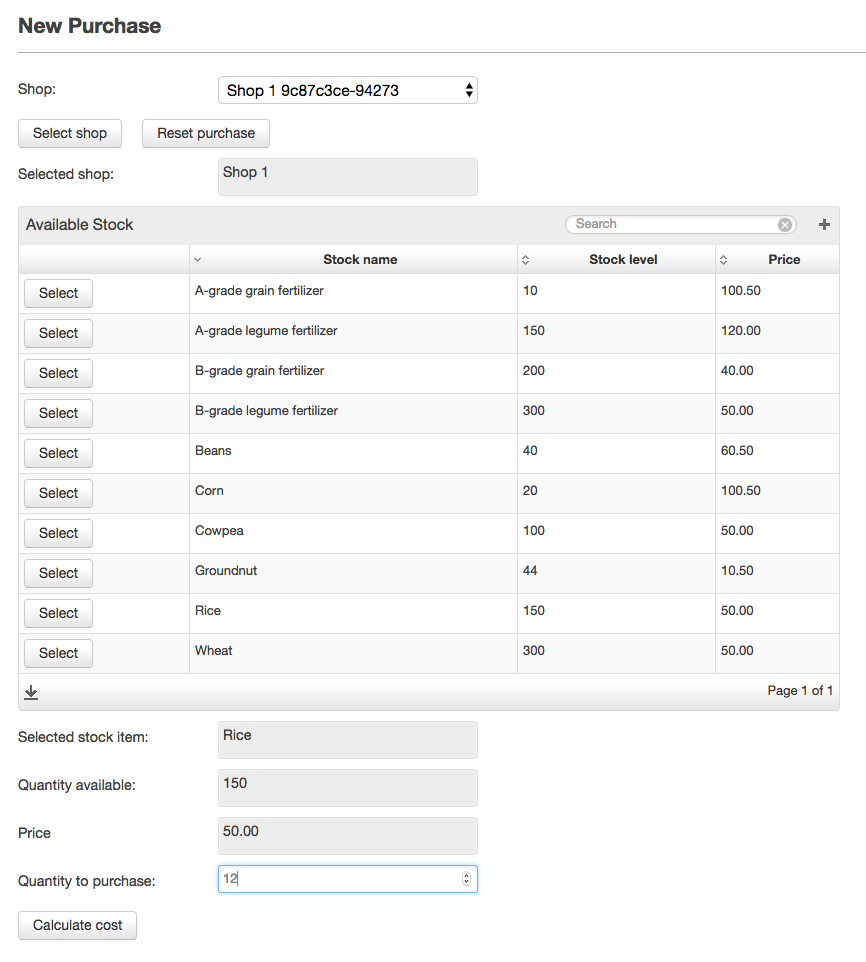 Image Added
Image Added
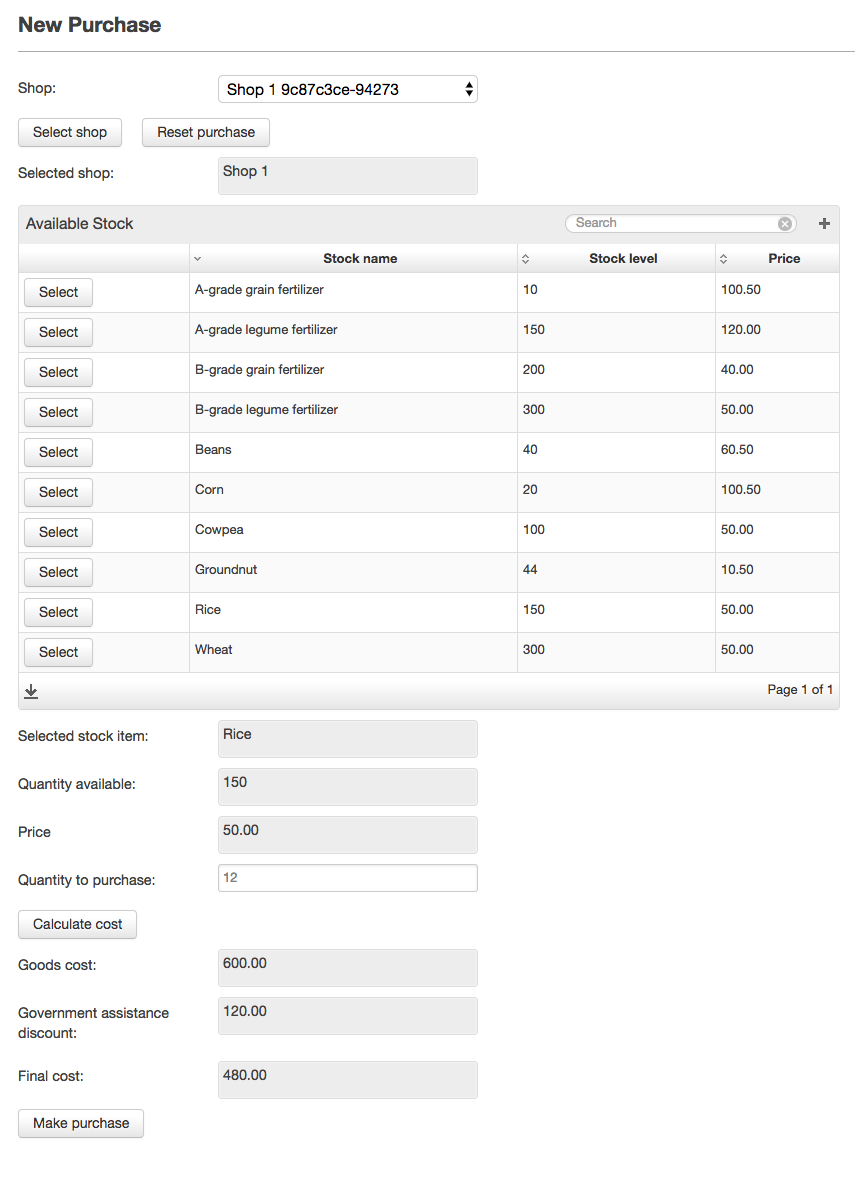 Image Added
Image Added
| Info |
|---|
Be careful when using visibility bindings on all your view components. If they all evaluate to false your view will fail to load instead of simply showing an empty view. |
| Info |
|---|
In cases where values are bound directly to primitive unit variables instead of model attributes, be sure to include manual validations using the Mez:alert functions seeing as data model validators cannot be used. |
Pay Built-In Functions
Once we have done all we need to do in our app to prepare for a payment the payment can be submitted to Helium by making a call to the pay built-in function. The following code snippet demonstrates this:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
farmerPurchase.paymentId = farmer.pay(shop, "KES", farmerPurchase.finalCost); |
In the code snippet above "farmer" is the payer and "shop" is the payee. Both the payer and payee needs to have an identifier. Depending on the Helium configuration for payments in the app this can be a so called "MSISDN". In our case, we have mobile number attributes on both the farmer and shop objects.
"KES" represents the currency for the payment. In this case Kenya shilling.
The amount that is being payed is retrieved from the "finalCost" attribute on our "farmerPurchase" object instance. Note that this has to be an int value.
The "pay" function returns a uuid that represents the internal Helium id for the payment. This, along with the @OnPaymentStatusUpdate annotation discussed later in the lesson, can be used to track the payment status in the app.
Outside of the actual DSL app, the Helium core app also provides a view showing payments submitted through Helium apps. This view can be used to reconcile any payments with the appropriate mPesa or other payment accounts that are in use.
In order to provide a reference between the payment as shown on this view and the payment in the app a further reference and message can be used.
Suppose we have an in app id for our purchase such as the Helium id for the FarmerPurchase object that we would also like to present as an additional unique reference for the payment. In addition we want to add the shop where the purchase happened as a non unique message to the Helium payment. This can be achieved using the "payWithRef" function:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
farmerPurchase.paymentId = farmer.payWithRef(
shop, "KES", farmerPurchase.finalCost, farmerPurchase._id,
Strings:concat(shop.name, " - ", shop.shopCode)
); |
Using the payWithRef function above, "farmerPurchase._id" represents the additional reference and the concatenated string represents an additional message. The message can also be left out by simply specifying an empty string literal.
| Info |
|---|
Note that some configuration is required in order for apps to be enabled to make payments. Contact Helium DevOps in order to have your app configured for making payments. |
| Info |
|---|
Note that some configuration is required in order for your Helium user to have access to the payment recon screen for specific apps and accounts. Contact Helium DevOps in order to have your user configured to view payments on the Helium core app payment recon screen. |
@OnPaymentUpdate Annotation for Payment Callback Functions
Helium processes payments asynchronously. This means that a result of a call to the pay function will not be immediately available.
Helium provides a mechanism whereby an app function can be declared as a callback that will be invoked once Helium has an update on the payment status. This is implemented by means of the @OnPaymentUpdate annotation. Such a callback for payments made without an additional reference is included in the app in the PaymentCallback presenter file and unit under the services folder:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
@OnPaymentUpdate
void paymentUpdate(uuid id, PAYMENT_STATUS status, string message){
// Find the associated purchase based on the internal Helium payment ID
// Ids should be unique so we are only expecting one purchase in the resulting collection
FarmerPurchase[] farmerPurchases = FarmerPurchase:equals(paymentId, id);
if(farmerPurchases.length() >= 0) {
FarmerPurchase farmerPurchase = farmerPurchases.first();
// Update the payment status maintained on the farmer purchase
farmerPurchase.paymentStatus = status;
// Record the time stamp of the update
farmerPurchase.paymentStatusUpdatedOn = Mez:now();
}
} |
For payments that were made with an additional reference we can change the function signature as follows:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
@OnPaymentUpdate
void paymentUpdateWithRef(uuid id, string reference, PAYMENT_STATUS status, string message){
.
.
} |
The HistoricFarmerPurchases view shows the purchase details for historic purchases including payment statuses as updated using the callback functions above. The screenshot below demonstrates this:
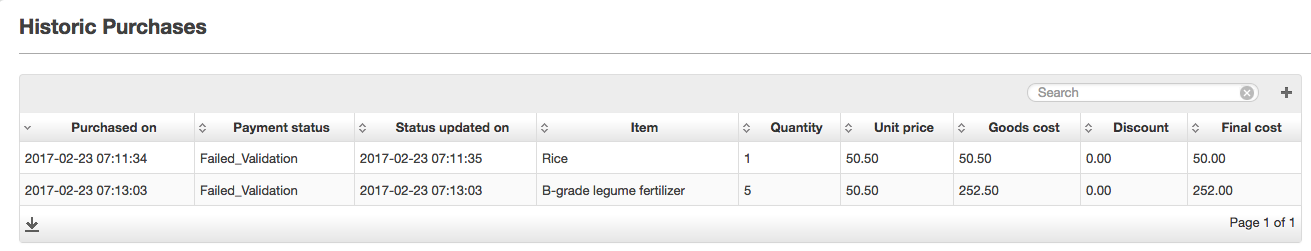 Image Added
Image Added
The payment status, as updated using the callback function, is "Failed_Validation" in this case. This is to be expected though as no configuration for the routing of payments in our app has been set. As summary of the possible statuses and their meanings follow below.
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Pending | An initial state indicating that the call to a pay function from the DSL application has been submitted and correctly interpreted by the back-end. |
| Registered | The payment has been received by the Helium payment framework and is being processed. |
| Failed_Validation | Processing of a payment contains a step where the provided information used in routing of the payment is validated. In some cases payments can use one of multiple accounts. If, during this step, the configuration for the application is read and applied and no matching account is found, the "Failed_Validation" status is returned. |
| Promise_To_Pay | The payment is confirmed to be valid and routable and, bar any network or other technical failures, will be paid. |
| Instructed | Communication has been completed between Helium and the payment gateway. |
| Result_Received | A result has been received from the payment gateway for processing the status. |
| Confirmed | Confirmed from the payment gateway result that the payment was a success. |
| Manual | Confirmed from the payment gateway result that payment was a failure. |
As a Farmer I want to purchase items from a shop and make payments using the Helium app
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Lesson Outcomes
By the end of this lesson you should:
- Be comfortable using visibility bindings to hide and show view components based on unit variables and functions
- Know what is required in order to make payments from an app and to track the status of these payments
- Know how to use the pay and payWithRef built-in functions
- Know how to use payment callback functions
App Use Case Scenario
The app use case for this lesson is that a farmer would like to make purchases from a specific shop using the application. This includes making a payment to the shop using the Helium payments framework.
Firstly, a farmer will select a shop and use a submit button to confirm his selection. The view will then be updated to display a table of all the stock items that a shop has in stock. This includes the name of the item, the current stock level and the current unit price for the stock item. The farmer will then select a stock item using a row action on this table.
Once this selection has been made, the view will again be updated to include info widgets showing the currently selected stock item, its stock level and unit price as well as a text area where the farmer can specify the quantity of the item he would like to purchase. Another submit button to calculate the total cost of the selection can then be pressed.
Once this has been done additional view components appear. These components describes a summary of the price for the goods, the discount offered if the farmer has previously uploaded a government assistance certificate and the final cost to the farmer. Once the farmer confirms this, the payment will be recorded and sent to Helium for processing using the payment framework.
Modified or Added
App Files
The files in the tutorial app that were modified or added as part of this lesson are as follows:
./model/objects/Shop.mez
./model/objects/FarmerPurchase.mez
./web-app/presenters/farmer_ops/FarmerPurchases.mez
./web-app/views/farmer_ops/HistoricFarmerPurchases.vxml
./web-app/views/farmer_ops/NewFarmerPurchase.vxml
./web-app/views/user_management/ShopOwnerDetails.vxml
./web-app/views/user_management/ShopOwnerUserMgmt.vxml
./web-app/lang/en.lang
./services/PaymentCallbacks.mez
Data Model Additions for Farmer Purchases
Only two additions to our date model is required. Firstly, an object to keep track of purchases made by farmers. This object needs to keep track of the purchase details such as item that was purchased, unit cost, discount and final cost. It also needs to keep track of the internal Helium payment status and id. This is discussed further later in this lesson. Further more, the object also need to keep track of the farmer, shop and stock item that was involved in the transaction.
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
persistent object FarmerPurchase {
// When was the purchase made
datetime purchasedOn;
// Quantity and cost of purchase
int quantity;
decimal unitPrice;
decimal goodsCost;
decimal discount;
int finalCost;
// Helium provided payment status and id
datetime paymentStatusUpdatedOn;
PAYMENT_STATUS paymentStatus;
uuid paymentId;
// Stock item that was purchased
@ManyToOne
Stock stock via purchases;
// Farmer that made the purchase
@ManyToOne
Farmer farmer via purchases;
// Shop at which purchase was made
@ManyToOne
Shop shop via purchases;
} |
Lastly, we also need to add a mobile number attribute to the Shop object. This is required for making payments to a specific shop.
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
@requiredFieldValidator("validator.required_field")
string mobileNumber; |
Overview of View and Unit Additions for Making Purchases
For the implementation of this feature we have added the NewFarmerPurchase view. This view has a menu item for the farmer role and is thus accessible from the main app menu. This single view will be used by the farmer to perform purchases from specific shops.
In addition a view containing all historic records, namely HistoricFarmerPurchaes, is also added and is accessible from an action button on the NewFarmerPurchase view.
These two views are backed by the FarmerPurchases presenter file and unit.
Widget Visibility
As mentioned in the scenario that accompanies this lesson, we will have multiple stages within the flow of the purchase feature. Despite this we will only be using one view. After each stage, more view components become visible to the user. This is achieved using "visbile" function bindings. The following code snippet shows the functions that are used for these bindings:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
// Once a shop has been selected, the stock items for this shop can be displayed
bool showStockTable() {
if(shop == null) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Once a stock item has been selected is can be displayed with a text field for the quantity to purchase
bool showPurchaseForm() {
if(showStockTable() == false || selectedStock == null) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Once the purchase quantity has been validated and the price calculated the cost summary can be displayed
bool showSummary() {
if(showPurchaseForm() == false || goodsCost == null) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
// In the case of a farmer with a government assistance certificate the discount related to this should
// also be shown as part of the final cost summary
bool governmentAssitanceApplicableAndSummary() {
if(showSummary() == false || farmer.governmentAssistanceCertificate == null) {
return false;
}
return true;
} |
The screenshots below show the difference stages of widget visibility for the NewFarmerPurchase view:




| Info |
|---|
Be careful when using visibility bindings on all your view components. If they all evaluate to false your view will fail to load instead of simply showing an empty view. |
| Info |
|---|
In cases where values are bound directly to primitive unit variables instead of model attributes, be sure to include manual validations using the Mez:alert functions seeing as data model validators cannot be used. |
Pay Built-In Functions
Once we have done all we need to do in our app to prepare for a payment the payment can be submitted to Helium by making a call to the pay built-in function. The following code snippet demonstrates this:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
farmerPurchase.paymentId = farmer.pay(shop, "KES", farmerPurchase.finalCost); |
In the code snippet above "farmer" is the payer and "shop" is the payee. Both the payer and payee needs to have an identifier. Depending on the Helium configuration for payments in the app this can be a so called "MSISDN". In our case, we have mobile number attributes on both the farmer and shop objects.
"KES" represents the currency for the payment. In this case Kenya shilling.
The amount that is being payed is retrieved from the "finalCost" attribute on our "farmerPurchase" object instance. Note that this has to be an int value.
The "pay" function returns a uuid that represents the internal Helium id for the payment. This, along with the @OnPaymentStatusUpdate annotation discussed later in the lesson, can be used to track the payment status in the app.
Outside of the actual DSL app, the Helium core app also provides a view showing payments submitted through Helium apps. This view can be used to reconcile any payments with the appropriate mPesa or other payment accounts that are in use.
In order to provide a reference between the payment as shown on this view and the payment in the app a further reference and message can be used.
Suppose we have an in app id for our purchase such as the Helium id for the FarmerPurchase object that we would also like to present as an additional unique reference for the payment. In addition we want to add the shop where the purchase happened as a non unique message to the Helium payment. This can be achieved using the "payWithRef" function:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
farmerPurchase.paymentId = farmer.payWithRef( shop, "KES", farmerPurchase.finalCost, farmerPurchase._id, Strings:concat(shop.name, " - ", shop.shopCode) ); |
Using the payWithRef function above, "farmerPurchase._id" represents the additional reference and the concatenated string represents an additional message. The message can also be left out by simply specifying an empty string literal.
| Info |
|---|
Note that some configuration is required in order for apps to be enabled to make payments. Contact Helium DevOps in order to have your app configured for making payments. |
| Info |
|---|
Note that some configuration is required in order for your Helium user to have access to the payment recon screen for specific apps and accounts. Contact Helium DevOps in order to have your user configured to view payments on the Helium core app payment recon screen. |
@OnPaymentUpdate Annotation for Payment Callback Functions
Helium processes payments asynchronously. This means that a result of a call to the pay function will not be immediately available.
Helium provides a mechanism whereby an app function can be declared as a callback that will be invoked once Helium has an update on the payment status. This is implemented by means of the @OnPaymentUpdate annotation. Such a callback for payments made without an additional reference is included in the app in the PaymentCallback presenter file and unit under the services folder:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
@OnPaymentUpdate
void paymentUpdate(uuid id, PAYMENT_STATUS status, string message){
// Find the associated purchase based on the internal Helium payment ID
// Ids should be unique so we are only expecting one purchase in the resulting collection
FarmerPurchase[] farmerPurchases = FarmerPurchase:equals(paymentId, id);
if(farmerPurchases.length() >= 0) {
FarmerPurchase farmerPurchase = farmerPurchases.first();
// Update the payment status maintained on the farmer purchase
farmerPurchase.paymentStatus = status;
// Record the time stamp of the update
farmerPurchase.paymentStatusUpdatedOn = Mez:now();
}
} |
For payments that were made with an additional reference we can change the function signature as follows:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
@OnPaymentUpdate
void paymentUpdateWithRef(uuid id, string reference, PAYMENT_STATUS status, string message){
.
.
} |
The HistoricFarmerPurchases view shows the purchase details for historic purchases including payment statuses as updated using the callback functions above. The screenshot below demonstrates this:

The payment status, as updated using the callback function, is "Failed_Validation" in this case. This is to be expected though as no configuration for the routing of payments in our app has been set. As summary of the possible statuses and their meanings follow below.
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Pending | An initial state indicating that the call to a pay function from the DSL application has been submitted and correctly interpreted by the back-end. |
| Registered | The payment has been received by the Helium payment framework and is being processed. |
| Failed_Validation | Processing of a payment contains a step where the provided information used in routing of the payment is validated. In some cases payments can use one of multiple accounts. If, during this step, the configuration for the application is read and applied and no matching account is found, the "Failed_Validation" status is returned. |
| Promise_To_Pay | The payment is confirmed to be valid and routable and, bar any network or other technical failures, will be paid. |
| Instructed | Communication has been completed between Helium and the payment gateway. |
| Result_Received | A result has been received from the payment gateway for processing the status. |
| Confirmed | Confirmed from the payment gateway result that the payment was a success. |
| Manual | Confirmed from the payment gateway result that payment was a failure. |